Who is Usually Involved In The Bullying? What Impact Do They Have?


By Antoine G Larosiliere
The more research I do and the more educators I speak to, I realize it’s important to know who is usually involved in the bullying?
I have a son who has been bullied, I have a younger son who got in trouble for bullying. Both of them have friends that were involved in bullying, but were they an innocent party in their friends situations? This is why the question of “who is usually involved in the bullying,” began to boggle my mind. Imagine if we as parents, students and educators truly understand the impact many have in a bullying situation. Well, I did some research and it’s time we find out. So, who is usually involved in the bullying? The answer is, most of us. The bully and the victim are obviously involved, with the bully intentionally trying to over power the victim by insulting, hurting, or embarrassing them. The Bully’s followers; who assist, but don’t start the bullying. The bully’s supporters; who support the bullying, but do not assist in it. The bullies passive supporters; who like the bullying, but don’t show obvious support. The bystanders; who just observe the bullying and do not stand against it. The potential defender; who wants to do something, but doesn’t. And the defenders; who dislike the bully or bullying and try to help the victim.
The bully
We should all have a pretty good idea by now on who the bully is. The bully is the person who is directly insulting, teasing, hurting, or embarrassing someone else. It doesn’t matter what type of bullying they are engaged in. Whether it be physical, social, psychological, sexual, prejudicial, cyber; as long as they are the aggressor or initiator, they’re the bully.
Impact:
These are the children whose own personal neglect or abuse has taught or compelled them to do the same thing to others. The children who try to control or impose their power on others, to have some remnants of control in their life. The main children, through no fault of their own, are in need of help to heal from their traumas.
“I myself was bullied early on in grammar school, and to survive it, I chose to become a bully for a period of time.”
The victim
The victims are also pretty obvious to identify. They are the person who is directly being hurt or affected by the bully. The kids who are a little different; overweight, short, wear glasses, and dress differently, kids who have the least friends, are not popular and who are seen as unwilling or unable to defend themselves, and even the kids who are awkward, lack confidence, and have low self esteem. By the way, many bullies also suffer from low self-esteem as well.
Impact:
These are the children that immediately get our attention because school systems are afraid of being sued and parents and educators are afraid of the long term effects the bullying may have on the child. Some of these effects include depression, suicide, and in many instances, may turn the victim into a bully. I myself was bullied early on in grammar school, and to survive it, I chose to become a bully for a period of time. It is very important to teach the victim how not to be a target and become more resilient. The article What Are Most Kids Bullied About, can serve as a useful resource on this matter.
The bully’s followers
The Bully’s followers are people who assist, but don’t start the bullying. The Bully’s supporters are bullies themselves. They tend to do the same or similar things as the bully, but because they didn’t start it, they are referred to as “followers.” They are also likely to have been victims of abuse themselves and have grown accustomed to such abuse. Some of them are afraid of the bully because they themselves at one point were hurt by the bully. Therefore, by assisting, the wrath of the bully will not be on them. These are the children who could potentially be the first to intervene.
Impact:
They are usually the bully’s friends and have firsthand knowledge of what the bully intends to do. Since they are bullies themselves, their actions magnify the bullies; making the abuse overwhelming for the victims.
“These are the “fans,” the bullies cheering section, the ones who validate the bullies actions.”
The bully’s supporters
The bully’s supporters support the bullying, but do not assist in it. The bully’s supporters, even though they don’t take an active role in the bullying, support it by being abound as the bullying is enacted. More specifically the ones who laugh and show visible amusement at the actions of the bully. They believe by not participating, they will avoid punishment, but the bully will allow them to stay in the circle.
Impact:
These are the “fans,” the bullies cheering section, the ones who validate the bullies’ actions. The bully loves the attention they get from the supporters and it fuels the bullies efforts to continue.
The bullies passive supporters
The bullies’ passive supporters are people who like the bullying, but don’t show obvious support. What does that mean? How do you like something but not show obvious support? Well, these are the main ones who engage in spreading the rumors and gossip. The ones who don’t hit the like button on the social media post, but will share it.
Impact:
By engaging in such behavior, the children show an indirect form of support. The spreading of rumors and the sharing of these posts breathe life into the longevity of the impact the bullying can have. Even after the bullying has stopped; rumors and gossiping, online or in person, is a constant reminder of what happens and deepens the trauma suffered by the victim.
“The people who grew up hearing “mind your own business,” yes that’s many of us.”
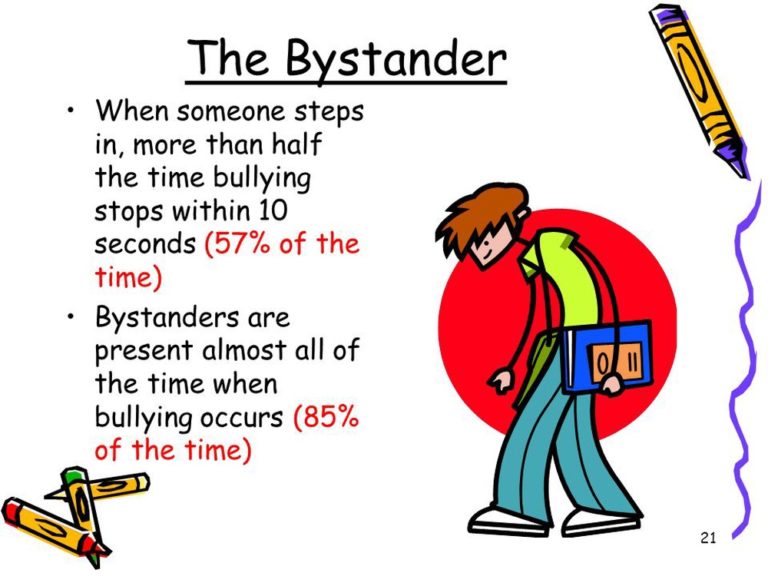
The bystander
The bystanders are children who just observe the bullying and do not stand against it.
The witnesses who witness the bullying but act like they saw nothing. The people who grew up hearing “mind your own business,” yes, that’s many of us. Their whole objective is to not be a witness, or not be involved in any kind of way. Studies show that bystanders are present 85% of the time when bullying occurs and the bullying stops within 10 seconds 57% of the time when a bystander steps in.
Impact:
Their presence is detrimental to the victim, because the bully understands that they will not acknowledge seeing any wrongdoings. Their lack or acknowledgment breeds an environment where violence perpetuates.
The potential defender
The potential defender dislikes bullying, wants to do something, but doesn’t. The potential defender is sympathetic to the victim, but struggles to find their own courage. They are fearful of retaliation, being labeled a “snitch” or being shunned by others. The potential defender’s likelihood of helping goes up if they’re the only witness. When they are other witnesses, their thought is, “maybe someone else will do something,” hoping to be bailed out by the other witnesses. In a well-known study, researchers found that, when bystanders were alone, 75 percent helped when they thought a person was in trouble. However, when a group of six people were together, only 31 percent helped.
Impact:
The potential defender essentially has the same impact as the bystander. They allow bullying to thrive in their presence. They have the potential to make a difference in the victims’ lives, but unfortunately fear for their own well being discourages them.
The defender
The defenders are people who dislike the bully or bullying and try to help the victim. They are our heroes! The ones who will look fear in the face and do what’s right. The ones who find courage and sacrifice their own security.
Impact:
The defenders appear to be the rarest in the bullying dynamic. They are special, and if we can encourage more bystanders and potential defenders to become defenders, it would greatly reduce the amount of bullying that occurs. More importantly, it would lessen the impact of the bullies’ actions. The victims’ trauma wouldn’t be as severe, because they would realize they are not alone and that their peers care about them.
Now that we know who is usually involved in the bullying and the impact they have, what do we do with this information?
–Educate your children: the more knowledgeable they are about the roles they play and their involvement in a bullying situation, the better choices they’ll make.
–Role Play: Role play at home different scenarios so children can become more comfortable with making better choices.
–Get Help: Get your children the appropriate help that they need to get over any trauma or abuse they are going through or have gone through. Speak to the teacher, guidance counselor, social worker, even your primary doctor, all hands on deck when it comes to our children.
I hope this has been helpful! Many strategies including the one I just mentioned can also be found in the novel The Bully Experience: Daniel’s Story . Also subscribe to the YouTube channel for more insight to these topics.
The Bully Experience "Daniel's Story"

Sign up for our newsletter and Read the novel For Free!
Stay updated. Sign up for our newsletter, and get the first two chapters of The Bully Experience Daniel’s Story absolutely free.